3D rendering can be defined as the computer-aided process by which computers convert 3D vector data into visual 2D images. This process is usually used to analyse virtual light sources reaction with various virtual material surfaces to produce photorealistic or other rendering styles.
Not only is 3D rendering important at the project early stages, but it is also crucial in communicating the feasibility of various ideas within the design team. Appealing visual communication of the possible product concepts not only acts as a proof of concept, but also helps in engineering the product. It also communicates how to put together or use the product. In order to achieve this feat, most designers and engineers rely on 3D rendering.
What is 3D rendering?
3D rendering usually refers to the creation of a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image of a concept using a computer program. Rendering may be 2D or 3D, depending on the designers need for idea conceptualisation. Rendering helps the designers in speeding up concept approval way before the actual product is made and also identify design problems. The rendered concept can also act as a marketing tool to attract potential customers or even investors.
Rendering software allows designers to create visuals that look as real as the end product, communicating the idea before a piece of material is even cut. This also helps designers and engineers collaborate on how best the end product can be made.
Design 3D Rendering
Rendering is becoming increasingly important in product design and development as it provides a better visual representation of the idea or concept. Designers are increasingly using rendering software at various stages in the product model development. It is used in the early stages of development to enable concept approval. The designer uses concept visuals to prove the quality of their new product. Later in the process, 3D rendered models are used to visually represent the desired completed product.
Designers make multiple views of the concept for use as sales, advertising and marketing materials. Companies use rendered images to test the reception of a new product to the public way before the actual product is completed. This also helps the designers make changes to the concept where needed. And this allows them to gather useful feedback before getting the product manufactured.
In this day of technological advancements, we will see more designers using rendering as proof of concept of new products. While photography isn’t going away anytime soon, rendering has become ubiquitous to new product development. Designers will continually look to better ways of representing their concepts, and it is quite clear that rendering is the way forward.
Photorealistic 3D rendering
Photography used to play a major role when companies wanted to bring ideas to life. Designers used to take pictures of prototypes as proof of concept. With the coming in of rendering software, photography in product development became overshadowed. 3D rendering makes the visualising of the idea much more realistic as compared to 2D photography.
Through rendering, the designer can decide exact aesthetics, which would require multiple shoots and sets to achieve with photography.
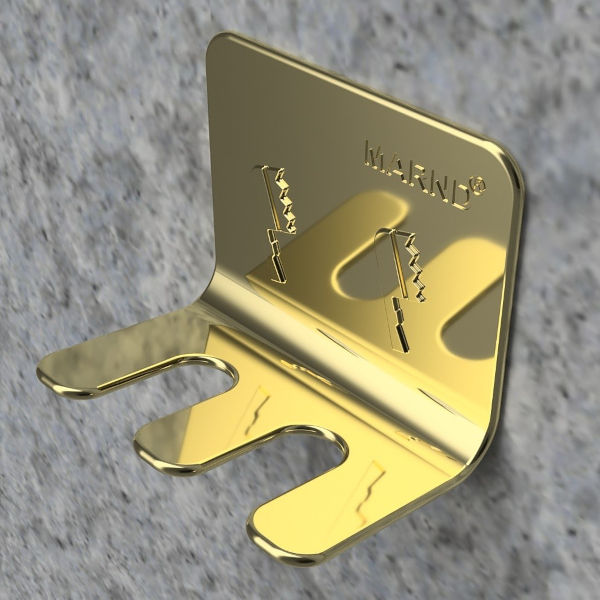

Rendering makes it easy to make changes to the visual concept, unlike photography, which is once-off and requires a new shoot to visualise changes made to the product. (I’m sure you can agree that this makes the process of coming up with a quality product easier and faster). Other engineering issues such as design problems can be easily detected through rendering software rather than photography.